zztop
Well-known member
Offline
This is why I have no faith in this country anymore

 www.nytimes.com
www.nytimes.com
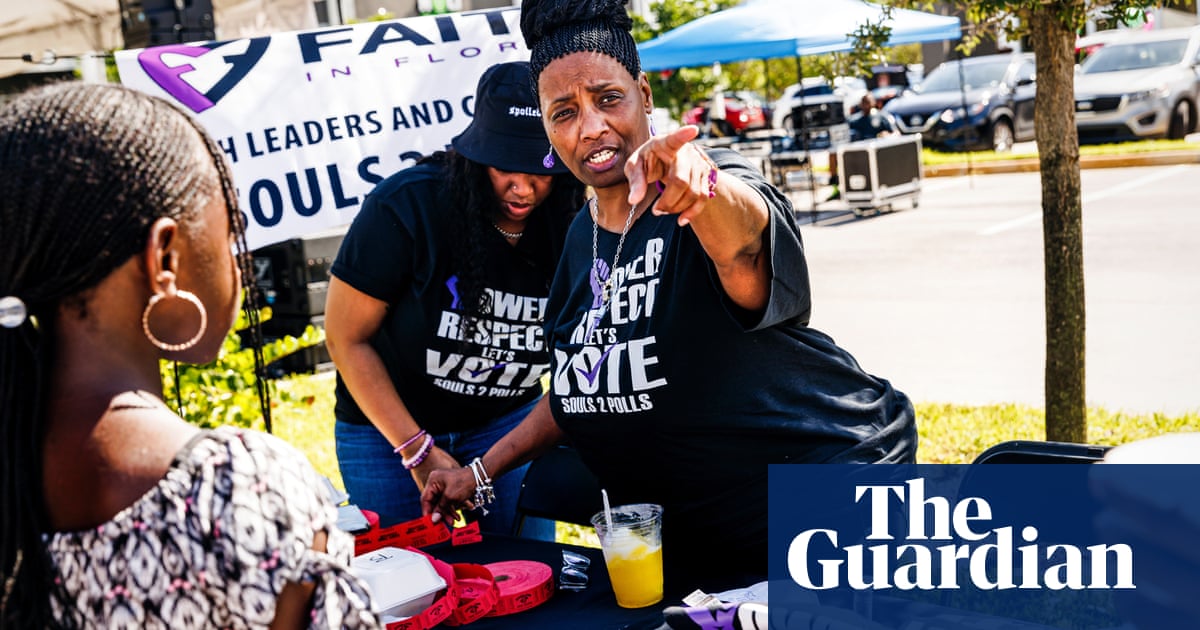
David Wasserman, who follows congressional redistricting for the Cook Political Report, said that using rejected maps in the four states, which make up nearly 10 percent of the seats in the House, was likely to hand Republicans five to seven House seats that they otherwise would not have won.
Some election law scholars say they are troubled by the consequences in the long run.
“We’re seeing a revolution in courts’ willingness to allow elections to go forward under illegal or unconstitutional rules,” Richard L. Hasen, a professor at the U.C.L.A. School of Law and the director of its Safeguarding Democracy Project, said in an interview. “And that’s creating a situation in which states are getting one free illegal election before they have to change their rules.”
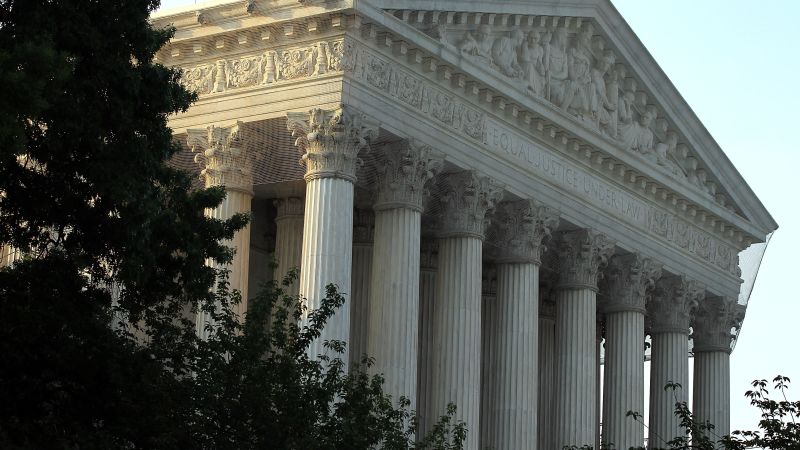
Behind much of the change is the Supreme Court’s embrace of an informal legal doctrine stating that judges should not order changes in election procedures too close to an actual election. In a 2006 case, Purcell v. Gonzalez, the court refused to stop an Arizona voter ID law from taking effect days before an election because that could “result in voter confusion and consequent incentive to remain away from the polls.”
The Purcell principle, as it is called, offers almost no guidance beyond that. But the Supreme Court has significantly broadened its scope in this decade, mostly through rulings on applications that seek emergency relief such as stays of lower court rulings, in which the justices’ reasoning often is cryptic or even unexplained.

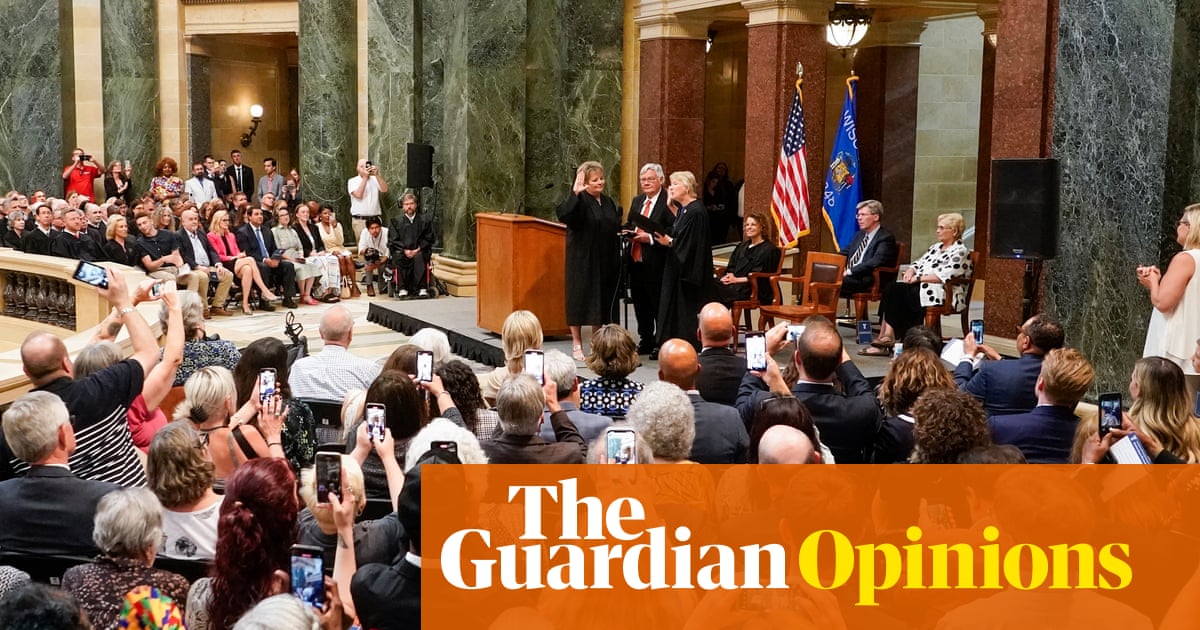
Maps in Four States Were Ruled Illegal Gerrymanders. They’re Being Used Anyway.
A Supreme Court shift, frowning on changes close to elections, gives House Republicans a big advantage in November.
David Wasserman, who follows congressional redistricting for the Cook Political Report, said that using rejected maps in the four states, which make up nearly 10 percent of the seats in the House, was likely to hand Republicans five to seven House seats that they otherwise would not have won.
Some election law scholars say they are troubled by the consequences in the long run.
“We’re seeing a revolution in courts’ willingness to allow elections to go forward under illegal or unconstitutional rules,” Richard L. Hasen, a professor at the U.C.L.A. School of Law and the director of its Safeguarding Democracy Project, said in an interview. “And that’s creating a situation in which states are getting one free illegal election before they have to change their rules.”
Behind much of the change is the Supreme Court’s embrace of an informal legal doctrine stating that judges should not order changes in election procedures too close to an actual election. In a 2006 case, Purcell v. Gonzalez, the court refused to stop an Arizona voter ID law from taking effect days before an election because that could “result in voter confusion and consequent incentive to remain away from the polls.”
The Purcell principle, as it is called, offers almost no guidance beyond that. But the Supreme Court has significantly broadened its scope in this decade, mostly through rulings on applications that seek emergency relief such as stays of lower court rulings, in which the justices’ reasoning often is cryptic or even unexplained.